NEWS & INSIGHTS | Opinion
UK’s largest battery project is coming, and it’s built to power ships too

This week in net zero: emissions progress, renewables investment shifts, giga-scale storage
Chief Technology Officer at NZTC, Luca Corradi, and his team closely monitor the global net zero landscape. They follow the trends, policies, investments and technological innovations that, together, bring the world closer to its shared climate goals. Learn more about our horizon scanning service. This week, Luca and his team look at emission reduction trends in UK oil and gas, shifts in the renewable energy market and an update on UK’s largest grid project.
UK Oil and Gas Emissions: Reduction Trends and North Sea Transition Deal Targets
Oil and gas meet around 75% of the UK’s energy demand and will remain an important part of the country’s energy mix for decades to come. North Sea emissions still account for just over 3% of total UK greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and production of most gas imported via pipeline results in fewer greenhouse gases per barrel than domestic production. The sector must continue to work hard on its commitments to reduce overall emissions.
The Emissions Monitoring Report 2025 shows UKCS upstream emissions fell by 7% between 2023 and 2024 – marking the fifth consecutive year of reductions and a 34% since 2018. Between 2018 and 2024, just over half of offshore emission reductions came from installations that remain operational, with the remainder linked to assets ceasing production.
In 2024, hydrocarbon combustion for power generation accounted for 80% of production emissions from offshore fields, followed by flaring (16%), venting (3%), and other non-combustion processes. Emissions from flaring dropped 4.8% in 2024, and were 51% lower than in 2018.
This progress puts the North Sea Transition Deal (NSTD) target of halving production emissions by 2030 well within reach. However, without serious investment in large-scale emissions abatement projects, the industry will miss its longer-term targets: a 90% reduction by 2040 and reach net zero by 2050.

GHG Emissions
Source: NSTA
Global Renewable Energy Investment 2025: Offshore Wind and Solar Market Shifts
Global investment in new renewable energy projects reached a record $386 billion in the first half (H1) of 2025 – up 10% from the previous year. Mainland China remained the largest market, accounting for 44% of total investment in H1 2025.
Offshore wind attracted $39 billion in H1 2025, surpassing the $31 billion total for all of 2024. This growth was driven by large-scale projects, the timing of government auctions, and elevated project costs outside mainland China.
In contrast, finance for utility-scale solar and onshore wind declined by 13% compared to H1 2024, marking the lowest share of total investment since 2006. Utility-scale solar was particularly affected, with investment falling 19%, as rising curtailment and increased exposure to negative prices discouraged investors.
Small-scale solar helped offset the decline in larger projects. In mainland China, investment in small-scale solar nearly doubled year-on-year, while utility-scale solar installations dropped 28% ahead of a regulatory shift that now exposes renewables to volatile power prices.
Among major regions, the United States saw the sharpest decline in new renewable energy investment in H1 2025, with committed spending down $20.5 billion (36%) from H2 2024. This reflects industry uncertainty following the 2024 US federal elections. In contrast, the EU-27 experienced a surge, with investment rising by nearly $30 billion (63%) compared to H2 2024. These figures suggest a reallocation of capital from the US to Europe, particularly in offshore wind.
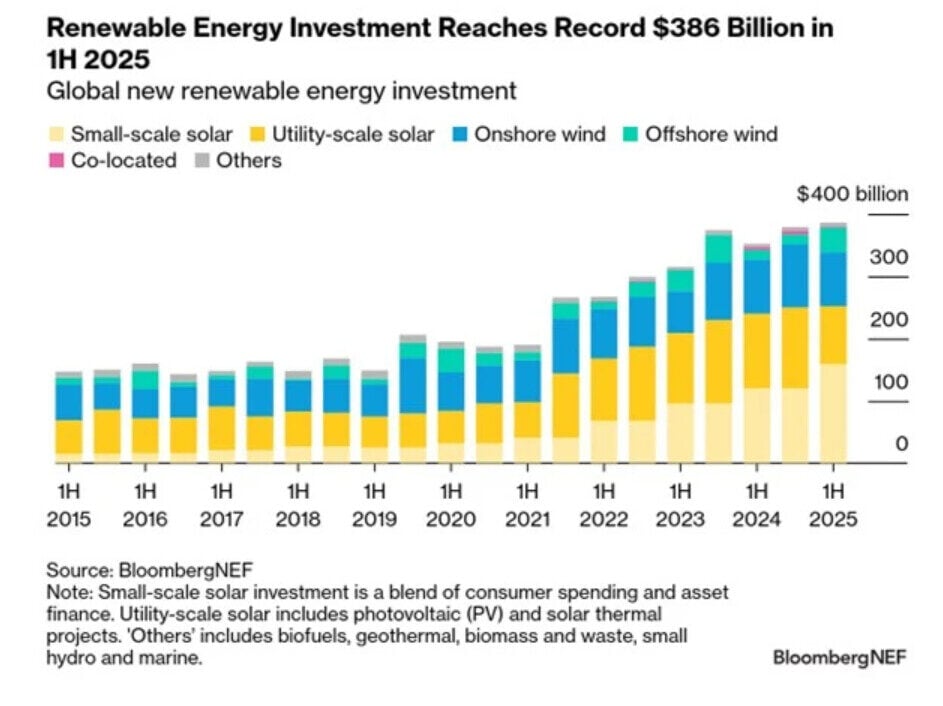
Global new renewable energy investment
Source: BloombergNEF
Teeside GigaPark BESS: UK’s Largest Grid Storage and Port Electrification Project
NatPower UK has signed an agreement with Sembcorp Utilities (UK) Limited to deliver a 1GW / 8GWh lithium-ion Battery Energy Storage System (BESS).
The £1 billion Teeside GigaPark is one of the UK’s highest-capacity and longest-duration energy storage projects. It’s also the first to combine utility-scale grid storage with dedicated port electrification infrastructure.
NatPower will build and operate the site, aiming to connect it to the grid by 2028. From the outset, the infrastructure is being designed to power ships at berth and recharge electric propulsion systems for future vessel types.
Initially, the GigaPark will operate with four hours of storage capacity (4GWh), with potential to double to eight hours (8GWh). Most UK BESS developments currently offer just two hours of storage, making this project a significant leap forward.
With electricity demand forecast to rise by 50% by 2050, and an additional 15% expected from shipping electrification, the UK grid faces unprecedented pressure. The Teeside GigaPark will help balance the grid and reduce curtailment, supporting a more resilient and flexible energy system.
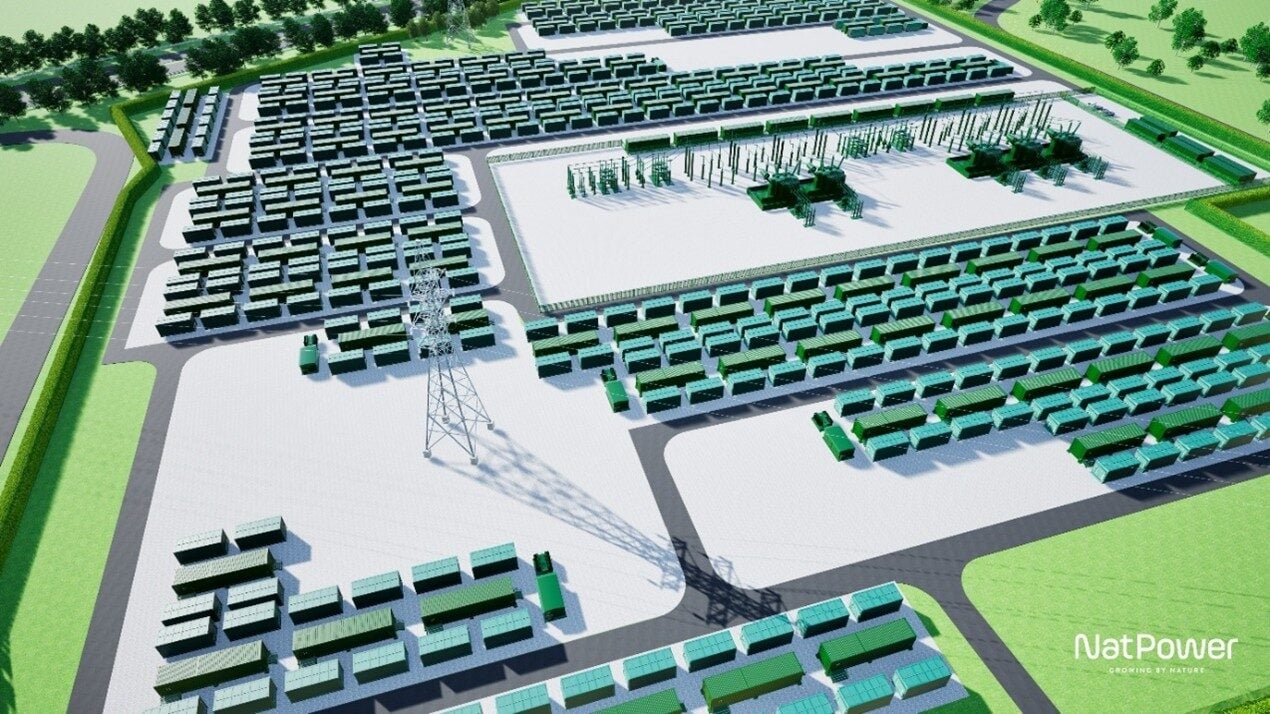

Artist’s Impression of Teesside GigaPark, Battery Storage Project on Sembcorp Utilities’ Wilton International Site
Source: NatPower
Subscribe for the latest updates





